The Invisible Shield: Understanding the Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere
Related Articles: The Invisible Shield: Understanding the Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Invisible Shield: Understanding the Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Invisible Shield: Understanding the Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere

The Earth’s atmosphere, a seemingly invisible blanket surrounding our planet, plays a crucial role in sustaining life. This gaseous layer is not a homogenous entity but rather a complex mixture of different gases, each with its unique properties and functions. Understanding the composition of this atmospheric "shield" is essential for comprehending the delicate balance that governs our planet’s climate, weather patterns, and the very existence of life.
A Symphony of Gases:
The Earth’s atmosphere is predominantly composed of nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2), accounting for approximately 78% and 21% respectively. These gases, along with other trace elements, form a dynamic system that interacts with various forces, including solar radiation, volcanic activity, and biological processes.
-
Nitrogen (N2): The dominant constituent of the atmosphere, nitrogen serves as an inert gas, playing a vital role in regulating temperature and atmospheric pressure. It also serves as a building block for essential biological molecules like proteins and nucleic acids.
-
Oxygen (O2): This essential gas is crucial for respiration, the process by which living organisms convert food into energy. Oxygen is also responsible for the formation of the ozone layer, which protects us from harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
Beyond the Major Players:
While nitrogen and oxygen dominate the atmospheric composition, a diverse array of other gases play significant roles in shaping our planet’s environment. These include:
-
Argon (Ar): A noble gas, argon is the third most abundant gas in the atmosphere, contributing to the overall atmospheric pressure.
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO2): This greenhouse gas plays a vital role in regulating Earth’s temperature. While essential for plant life through photosynthesis, rising CO2 levels due to human activities are contributing to global warming.
-
Water Vapor (H2O): The concentration of water vapor varies significantly depending on location and temperature. It is a crucial component of the water cycle, influencing cloud formation, precipitation, and weather patterns.
-
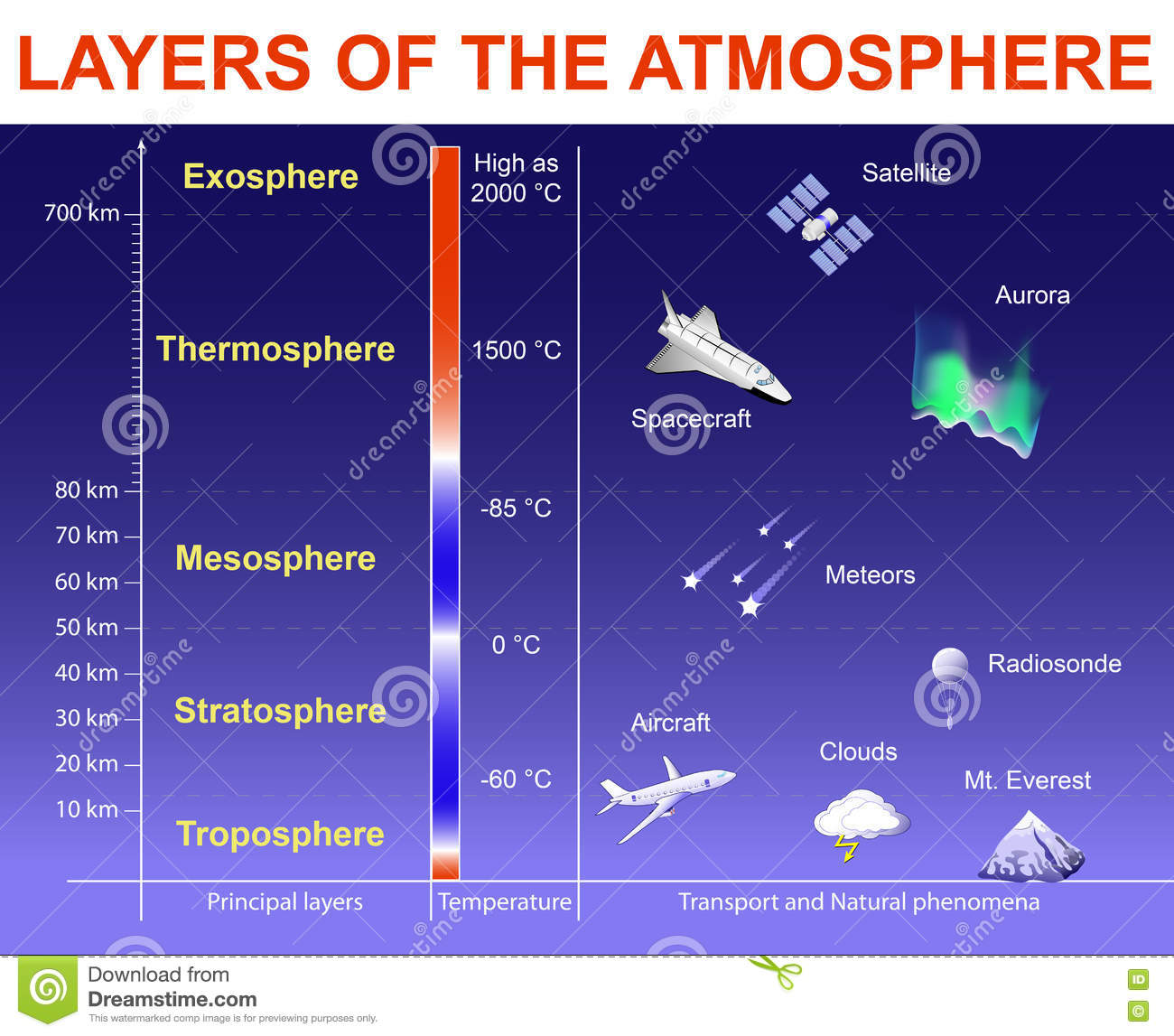
Ozone (O3): This gas, found primarily in the stratosphere, acts as a shield against harmful ultraviolet radiation. However, ozone in the lower atmosphere, known as ground-level ozone, is a pollutant that can damage human health and the environment.
-
Other Trace Gases: In addition to these major constituents, the atmosphere contains trace amounts of other gases, including methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and sulfur dioxide (SO2). These gases, while present in small quantities, can have significant environmental impacts.
The Dynamic Nature of the Atmosphere:
The composition of the atmosphere is not static but constantly evolving due to a complex interplay of natural and human-induced processes. Volcanic eruptions, for instance, can release significant amounts of sulfur dioxide and other gases into the atmosphere, influencing climate patterns. Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, are also altering the atmospheric composition, leading to increased levels of greenhouse gases and potentially contributing to climate change.
The Importance of Atmospheric Composition:
The composition of the Earth’s atmosphere is a vital factor in sustaining life. It provides a protective shield against harmful radiation, regulates temperature, and supports weather patterns that enable diverse ecosystems to thrive. Understanding the delicate balance of atmospheric gases and the factors influencing their composition is crucial for addressing global challenges like climate change and protecting the environment.
FAQs on Atmospheric Composition:
1. What is the most abundant gas in the Earth’s atmosphere?
Nitrogen (N2) is the most abundant gas, accounting for roughly 78% of the atmosphere’s composition.
2. How does the atmosphere protect us from harmful radiation?
The ozone layer, located in the stratosphere, absorbs most of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation, shielding life on Earth from its damaging effects.
3. What is the role of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, meaning it traps heat in the atmosphere. While essential for plant life, rising CO2 levels due to human activities are contributing to global warming.
4. How does water vapor influence weather patterns?
Water vapor is a crucial component of the water cycle. It influences cloud formation, precipitation, and temperature variations, shaping weather patterns across the globe.
5. What are the potential consequences of changes in atmospheric composition?
Changes in atmospheric composition, particularly increased greenhouse gas concentrations, can lead to climate change, impacting weather patterns, sea levels, and ecosystems worldwide.
Tips for Understanding Atmospheric Composition:
- Visualize the atmosphere: Imagine the atmosphere as a series of layers, each with unique characteristics and functions.
- Focus on the major gases: Understand the roles of nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide in sustaining life and regulating climate.
- Explore the interconnectedness: Recognize that the atmosphere is a dynamic system where different gases interact and influence each other.
- Stay informed about climate change: Learn about the impact of human activities on atmospheric composition and the consequences for our planet.
Conclusion:
The Earth’s atmosphere, a seemingly invisible shield, is a complex and dynamic system that sustains life. Understanding the composition of this gaseous layer, the roles of different gases, and the factors influencing their balance is crucial for comprehending the delicate balance of our planet’s climate and environment. As we navigate the challenges of climate change and environmental protection, a deeper understanding of the atmosphere and its composition is more important than ever.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Invisible Shield: Understanding the Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!