The Hemapophyseal Joint: A Vital Component of the Spine’s Stability and Mobility
Related Articles: The Hemapophyseal Joint: A Vital Component of the Spine’s Stability and Mobility
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Hemapophyseal Joint: A Vital Component of the Spine’s Stability and Mobility. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Hemapophyseal Joint: A Vital Component of the Spine’s Stability and Mobility

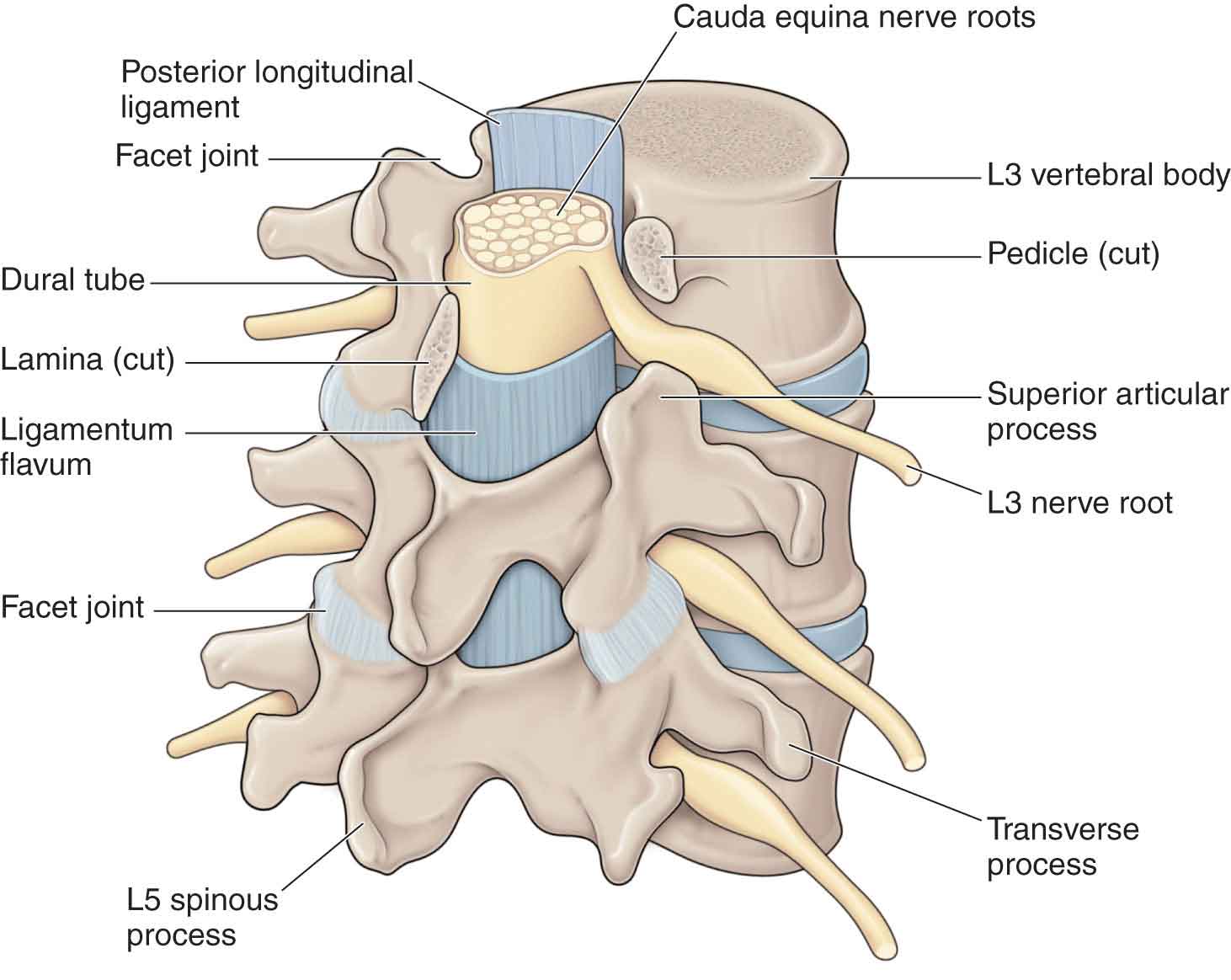
The human spine, a complex and intricate structure, is responsible for supporting the body’s weight, providing flexibility, and protecting the delicate spinal cord. This complex system relies on a network of interconnecting elements, one of which is the hemapophyseal joint, also known as the facet joint. These joints, often overlooked, play a crucial role in maintaining spinal stability and enabling the wide range of movements we perform daily.
Understanding the Hemapophyseal Joint
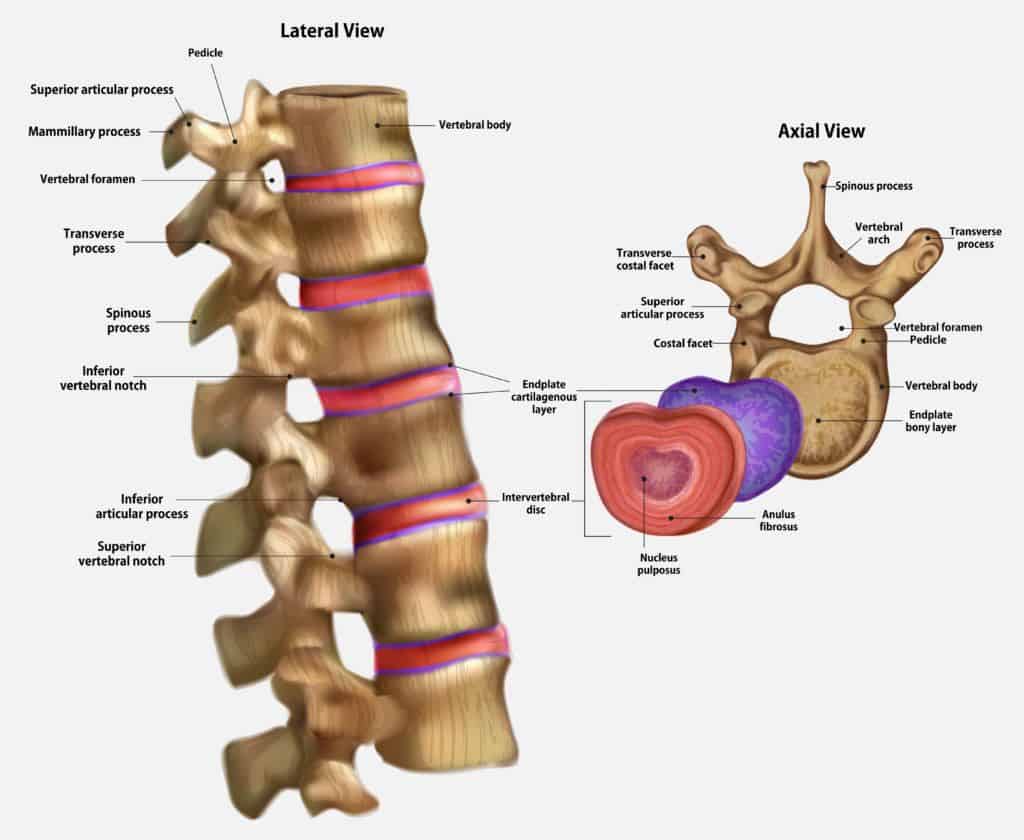
The hemapophyseal joint is a synovial joint, characterized by a smooth cartilage lining and a fluid-filled cavity that facilitates frictionless movement. Located between the bony projections called articular processes, these joints connect adjacent vertebrae, forming a complex network of articulations that extends the length of the spine.
Each vertebra, the individual bony units that make up the spine, possesses two superior and two inferior articular processes. These processes, shaped like small, smooth knobs, form the articulation points for the hemapophyseal joints. These joints, found throughout the spine, are essential for:
- Stability: The hemapophyseal joints restrict excessive movement between vertebrae, providing stability and preventing injury. They act as a guide, limiting the range of motion in each segment and ensuring the spine functions as a cohesive unit.
- Mobility: While providing stability, these joints also contribute to the spine’s flexibility. They allow for controlled movements such as flexion, extension, rotation, and lateral bending, crucial for everyday activities like walking, turning, and reaching.
- Proprioception: The hemapophyseal joints contain sensory receptors that provide information about the position and movement of the spine. This feedback loop allows the brain to monitor and adjust spinal movements, contributing to balance and coordination.
The Hemapophyseal Joint in Different Regions of the Spine
The structure and function of the hemapophyseal joints vary slightly depending on their location within the spine.
- Cervical Spine: The hemapophyseal joints in the cervical spine, the neck region, are oriented at a 45-degree angle, facilitating a wide range of motion. This allows for the head’s flexibility, enabling us to look up, down, and sideways.
- Thoracic Spine: The hemapophyseal joints in the thoracic spine, the mid-back region, are oriented vertically, limiting rotation and providing greater stability. This supports the rib cage and facilitates breathing.
- Lumbar Spine: The hemapophyseal joints in the lumbar spine, the lower back region, are oriented in a more horizontal plane, allowing for greater flexion and extension. This allows for the flexibility needed for bending and lifting.
Common Conditions Affecting the Hemapophyseal Joint
Despite their robust design, hemapophyseal joints are susceptible to several conditions that can affect their function and cause pain. These include:
- Facet Joint Arthritis: This degenerative condition occurs when the cartilage lining the joint wears down, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility.
- Facet Joint Syndrome: This refers to a range of symptoms caused by irritation or inflammation of the facet joint, often resulting from overuse, injury, or degeneration.
- Facet Joint Sprain: This is a sudden injury to the ligaments surrounding the facet joint, often caused by a whiplash injury or a sudden twisting movement.
- Facet Joint Impingement: This occurs when the joint space narrows, leading to compression of nerves and blood vessels, causing pain and numbness.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Hemapophyseal Joint Conditions
Diagnosing conditions affecting the hemapophyseal joint often involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies, and sometimes nerve conduction tests. Treatment options vary depending on the specific condition and severity.
- Conservative Treatment: This includes rest, ice, compression, elevation, pain medications, physical therapy, and steroid injections.
- Surgical Treatment: In cases of severe pain, instability, or nerve compression, surgery may be necessary to address the underlying condition. This might involve fusion of the affected vertebrae or decompression of the nerves.
Preventing Hemapophyseal Joint Problems
Maintaining a healthy spine is crucial for preventing problems with the hemapophyseal joints. Here are some tips:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts additional stress on the spine, increasing the risk of joint degeneration.
- Practice Good Posture: Proper posture helps distribute weight evenly, minimizing stress on the joints.
- Engage in Regular Exercise: Strengthening the muscles that support the spine and improving flexibility can help prevent injuries and maintain joint health.
- Avoid Overuse and Repetitive Movements: Repeated stress on the spine can lead to joint inflammation and degeneration.
- Use Proper Lifting Techniques: Lifting heavy objects with proper technique minimizes strain on the spine.
Conclusion
The hemapophyseal joint, a critical component of the spinal structure, plays a vital role in maintaining stability, enabling mobility, and providing proprioception. Understanding the function and potential problems affecting these joints is essential for maintaining spinal health. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, practicing good posture, and engaging in regular exercise, individuals can minimize the risk of developing hemapophyseal joint conditions and enjoy a pain-free, mobile spine throughout life.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Hemapophyseal Joint
1. What is the difference between a hemapophyseal joint and a facet joint?
The terms "hemapophyseal joint" and "facet joint" are often used interchangeably, as they refer to the same structure. However, "hemapophyseal joint" is a more technical term derived from the anatomical structures involved, while "facet joint" is a more commonly used term.
2. Are hemapophyseal joint problems common?
While not as widely discussed as other spinal conditions, hemapophyseal joint problems are relatively common, especially as people age. Degenerative changes, overuse, and injuries can all contribute to joint pain and dysfunction.
3. How can I tell if I have a problem with my hemapophyseal joints?
Symptoms of hemapophyseal joint problems can include pain, stiffness, decreased range of motion, muscle spasms, and radiating pain into the arms or legs. If you experience these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
4. What are the most common treatments for hemapophyseal joint problems?
Treatment options for hemapophyseal joint problems vary depending on the severity and underlying cause. Conservative treatments, such as pain medications, physical therapy, and steroid injections, are often effective. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
5. Can I prevent hemapophyseal joint problems?
While some factors, such as age and genetics, are beyond our control, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of developing hemapophyseal joint problems. Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding overuse can all help protect the joints.
6. What are the long-term implications of hemapophyseal joint problems?
Untreated hemapophyseal joint problems can lead to chronic pain, decreased mobility, and difficulty with daily activities. In some cases, they can also contribute to nerve compression and other complications. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing these conditions and preventing further deterioration.
7. Can I continue to exercise if I have hemapophyseal joint problems?
Yes, exercise can be beneficial for managing hemapophyseal joint problems. However, it’s important to choose exercises that are safe and appropriate for your condition. Consult a physical therapist or healthcare professional to develop a personalized exercise plan.
8. Are there any specific exercises that can help with hemapophyseal joint problems?
Physical therapists can recommend specific exercises to strengthen the muscles that support the spine, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. These may include core strengthening exercises, stretching, and low-impact aerobic activities.
9. What are the latest advancements in treating hemapophyseal joint problems?
Advances in minimally invasive surgical techniques and regenerative medicine offer promising solutions for treating hemapophyseal joint problems. These approaches aim to address the underlying cause of pain and restore joint function with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues.
10. What are the long-term effects of surgical treatment for hemapophyseal joint problems?
The long-term effects of surgery vary depending on the specific procedure and individual factors. In many cases, surgery can provide significant pain relief and improve mobility. However, it’s important to discuss potential risks and complications with a qualified surgeon before proceeding.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Hemapophyseal Joint: A Vital Component of the Spine’s Stability and Mobility. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!