Hematopoiesis: The Symphony of Blood Cell Production
Related Articles: Hematopoiesis: The Symphony of Blood Cell Production
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Hematopoiesis: The Symphony of Blood Cell Production. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Hematopoiesis: The Symphony of Blood Cell Production
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Hematopoiesis: The Symphony of Blood Cell Production
- 3.1 The Hematopoietic Stem Cell: The Master Conductor
- 3.2 The Orchestration of Hematopoiesis: A Multi-Step Process
- 3.3 The Regulatory Symphony: Factors Orchestrating Hematopoiesis
- 3.4 The Importance of Hematopoiesis: A Vital Symphony for Life
- 3.5 Dysfunctional Hematopoiesis: When the Symphony Goes Off-Key
- 3.6 Understanding Hematopoiesis: A Key to Treatment and Research
- 3.7 FAQs about Hematopoiesis
- 3.8 Tips for Maintaining Healthy Hematopoiesis
- 3.9 Conclusion: The Symphony of Life
- 4 Closure
Hematopoiesis: The Symphony of Blood Cell Production
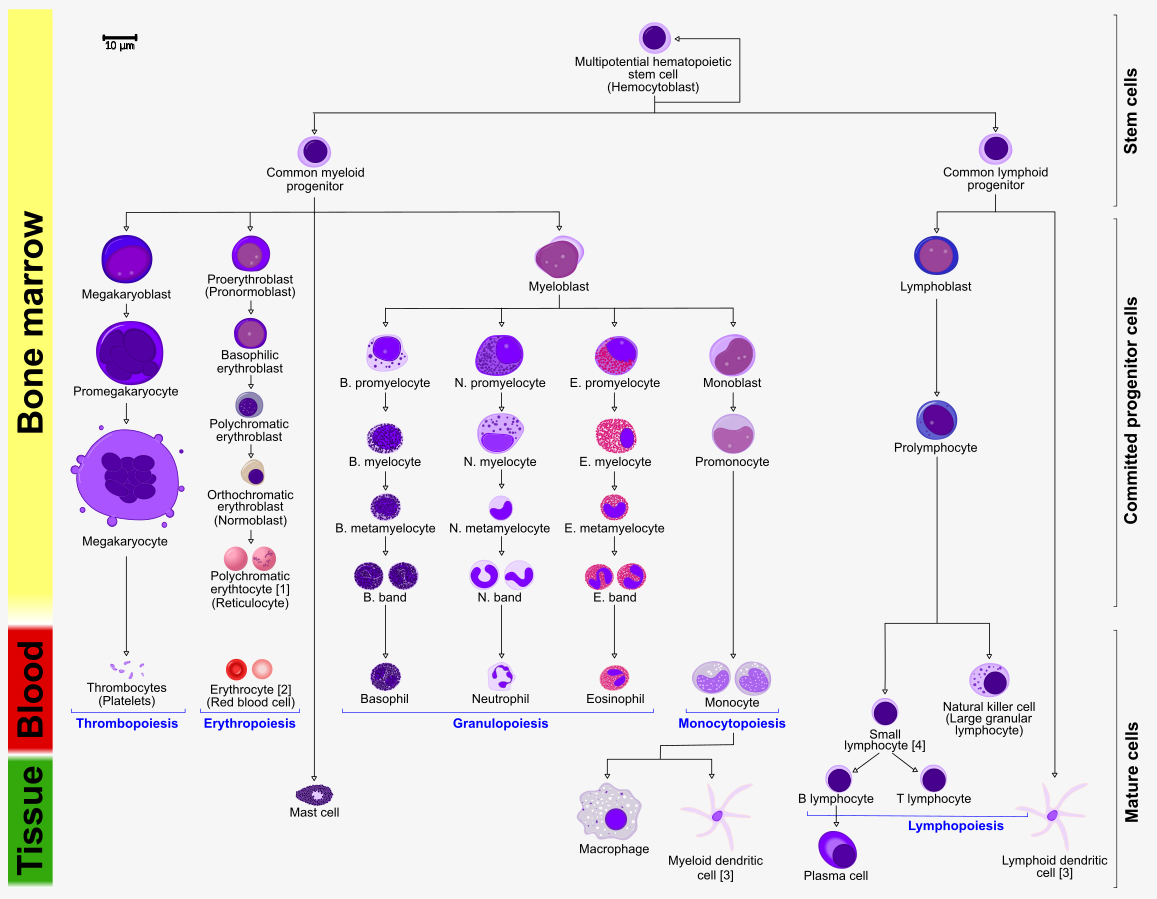
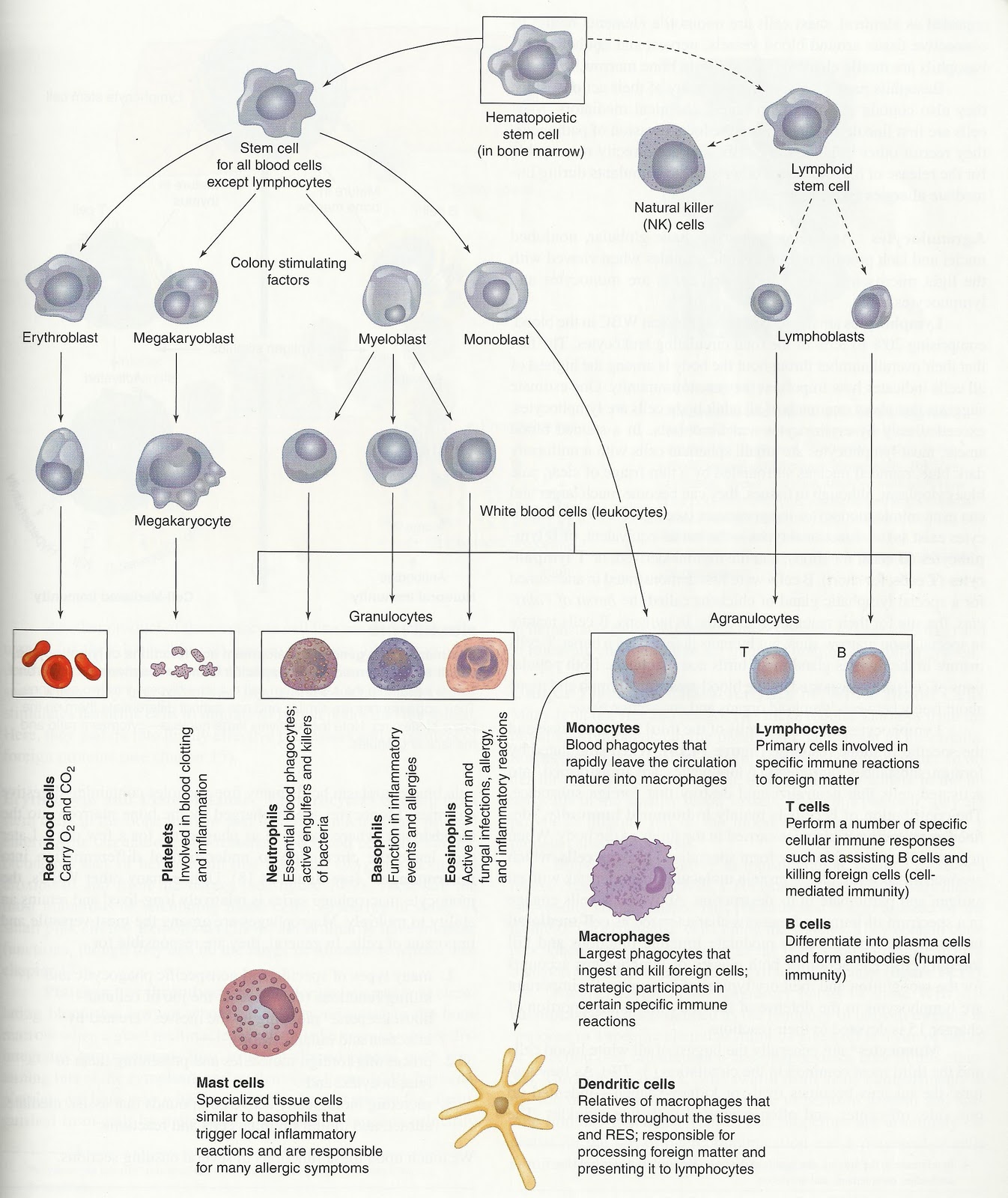
Hematopoiesis, a term derived from the Greek words "haima" (blood) and "poiesis" (creation), refers to the complex and continuous process of blood cell formation. This intricate symphony of cellular differentiation occurs within the bone marrow, a spongy tissue found within the hollow cavities of bones. Hematopoiesis is essential for maintaining the body’s delicate balance, ensuring a constant supply of red blood cells for oxygen transport, white blood cells for immune defense, and platelets for blood clotting.
The Hematopoietic Stem Cell: The Master Conductor
At the heart of hematopoiesis lies the hematopoietic stem cell (HSC), a remarkable cell with the remarkable ability to self-renew and differentiate into all types of blood cells. These versatile cells reside in the bone marrow, constantly dividing and giving rise to a diverse array of blood cell lineages.
The Orchestration of Hematopoiesis: A Multi-Step Process
Hematopoiesis is not a single event but a carefully orchestrated cascade of events involving several stages:
-
Commitment: HSCs receive signals from their environment, guiding them to commit to a specific blood cell lineage, such as erythroid (red blood cells), myeloid (white blood cells and platelets), or lymphoid (lymphocytes).
-
Proliferation: Committed progenitor cells undergo rapid proliferation, expanding the pool of cells destined for a particular lineage.
-
Differentiation: Progenitor cells undergo a series of differentiation steps, gradually acquiring the specialized features and functions of mature blood cells.
-
Maturation: Mature blood cells, fully equipped with their specific functions, are released into the bloodstream, where they circulate and perform their vital roles.
The Regulatory Symphony: Factors Orchestrating Hematopoiesis
Hematopoiesis is not a haphazard process but is tightly regulated by a complex interplay of factors:
-
Growth factors: These proteins, such as erythropoietin (EPO) for red blood cell production and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) for white blood cell production, act as chemical messengers, stimulating proliferation and differentiation of specific blood cell lineages.
-
Cytokines: These signaling molecules, produced by various cells in the body, play a crucial role in coordinating the intricate network of hematopoietic processes.
-
Microenvironment: The bone marrow microenvironment provides a supportive niche for HSCs and their progeny, offering physical support, growth factors, and other essential factors.
The Importance of Hematopoiesis: A Vital Symphony for Life
Hematopoiesis is essential for survival, ensuring the continuous production of blood cells vital for:
-
Oxygen transport: Red blood cells, packed with hemoglobin, carry oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues.
-
Immune defense: White blood cells, the body’s soldiers, protect against infections and diseases.
-
Blood clotting: Platelets, tiny cell fragments, help stop bleeding by forming clots at the site of injury.
Dysfunctional Hematopoiesis: When the Symphony Goes Off-Key
Disruptions in hematopoiesis can lead to a range of health problems, including:
-
Anemia: A deficiency in red blood cells, resulting in fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
-
Leukemia: A type of cancer affecting the blood-forming cells, leading to an overproduction of abnormal white blood cells.
-
Thrombocytopenia: A low platelet count, increasing the risk of bleeding.
Understanding Hematopoiesis: A Key to Treatment and Research
Understanding the intricate mechanisms of hematopoiesis is crucial for:
-
Diagnosis and treatment of blood disorders: By identifying the underlying cause of hematopoietic dysfunction, physicians can develop effective treatment strategies.
-
Stem cell transplantation: Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation offers hope for patients with blood disorders, replacing damaged or diseased blood-forming cells with healthy ones.
-
Drug development: Research into hematopoiesis is leading to the development of new drugs that stimulate blood cell production or target specific pathways involved in hematopoietic disorders.
FAQs about Hematopoiesis
Q: Where does hematopoiesis occur?
A: Hematopoiesis primarily occurs within the bone marrow, the spongy tissue found inside the hollow cavities of bones.
Q: What are hematopoietic stem cells?
A: Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are multipotent cells residing in the bone marrow, capable of self-renewal and differentiation into all types of blood cells.
Q: What is the role of growth factors in hematopoiesis?
A: Growth factors, such as EPO and G-CSF, act as chemical messengers, stimulating the proliferation and differentiation of specific blood cell lineages.
Q: What are some common disorders related to hematopoiesis?
A: Common hematopoietic disorders include anemia, leukemia, and thrombocytopenia.
Q: What are the potential benefits of research into hematopoiesis?
A: Research into hematopoiesis can lead to improved diagnosis and treatment of blood disorders, development of new therapies, and advancements in stem cell transplantation.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Hematopoiesis
-
Maintain a balanced diet: Consume a diet rich in iron, vitamin B12, and folate, essential nutrients for red blood cell production.
-
Engage in regular exercise: Exercise promotes healthy blood flow and circulation, supporting overall hematopoiesis.
-
Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: These habits can negatively impact bone marrow function and hematopoiesis.
-
Get regular medical checkups: Regular blood tests can detect early signs of hematopoietic disorders.
Conclusion: The Symphony of Life
Hematopoiesis is a complex and vital process, ensuring a constant supply of blood cells essential for life. Understanding the intricate mechanisms of this symphony of cellular differentiation is crucial for diagnosis, treatment, and research into blood disorders. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and seeking regular medical care, individuals can contribute to the harmonious functioning of their own hematopoietic system.
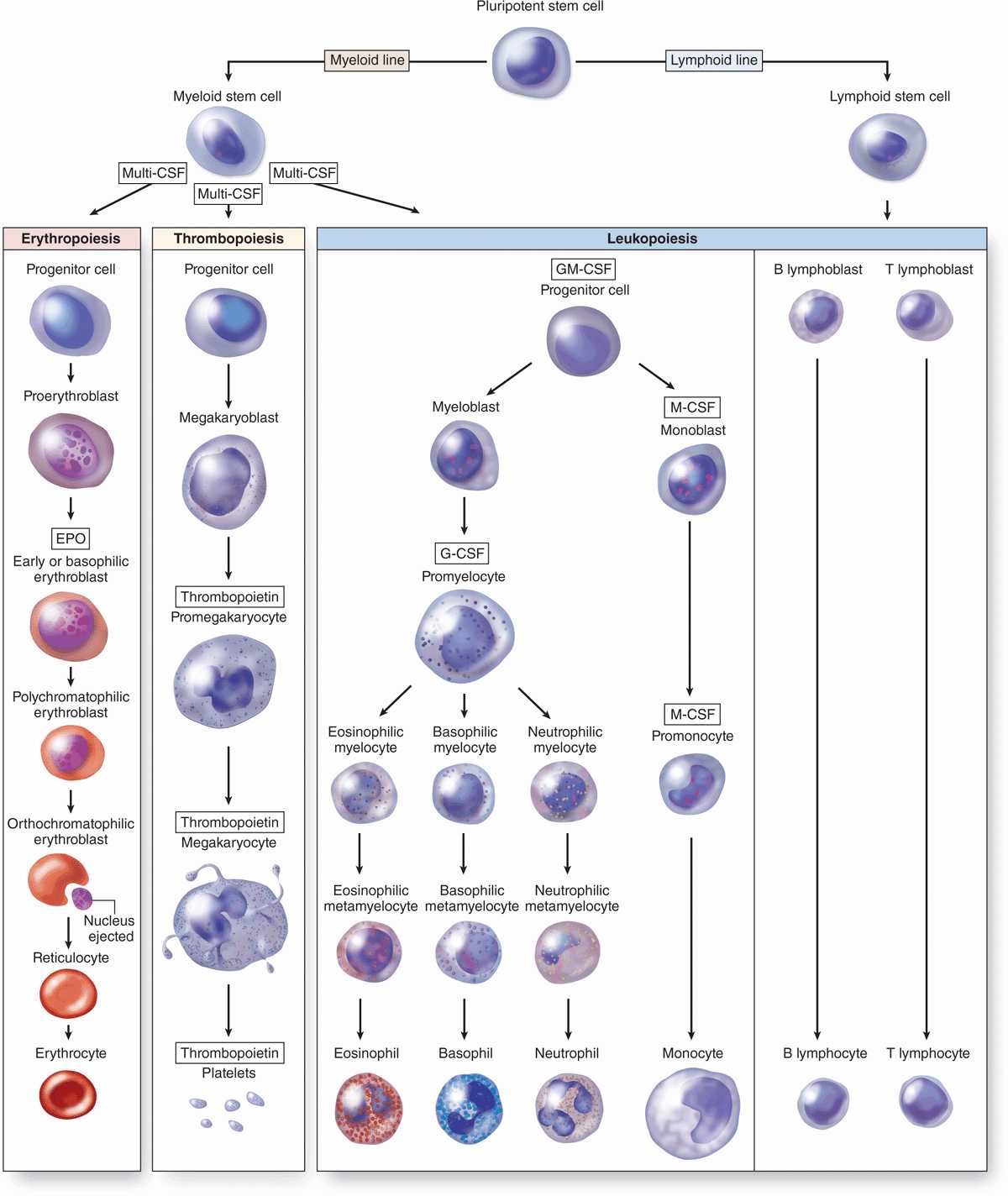

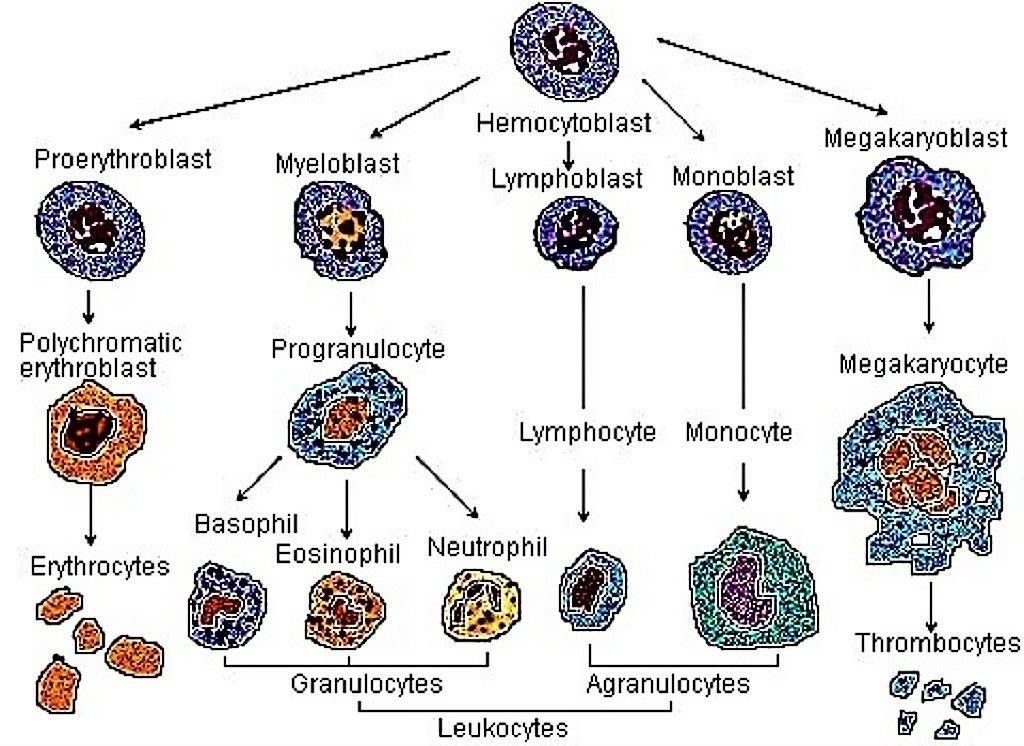



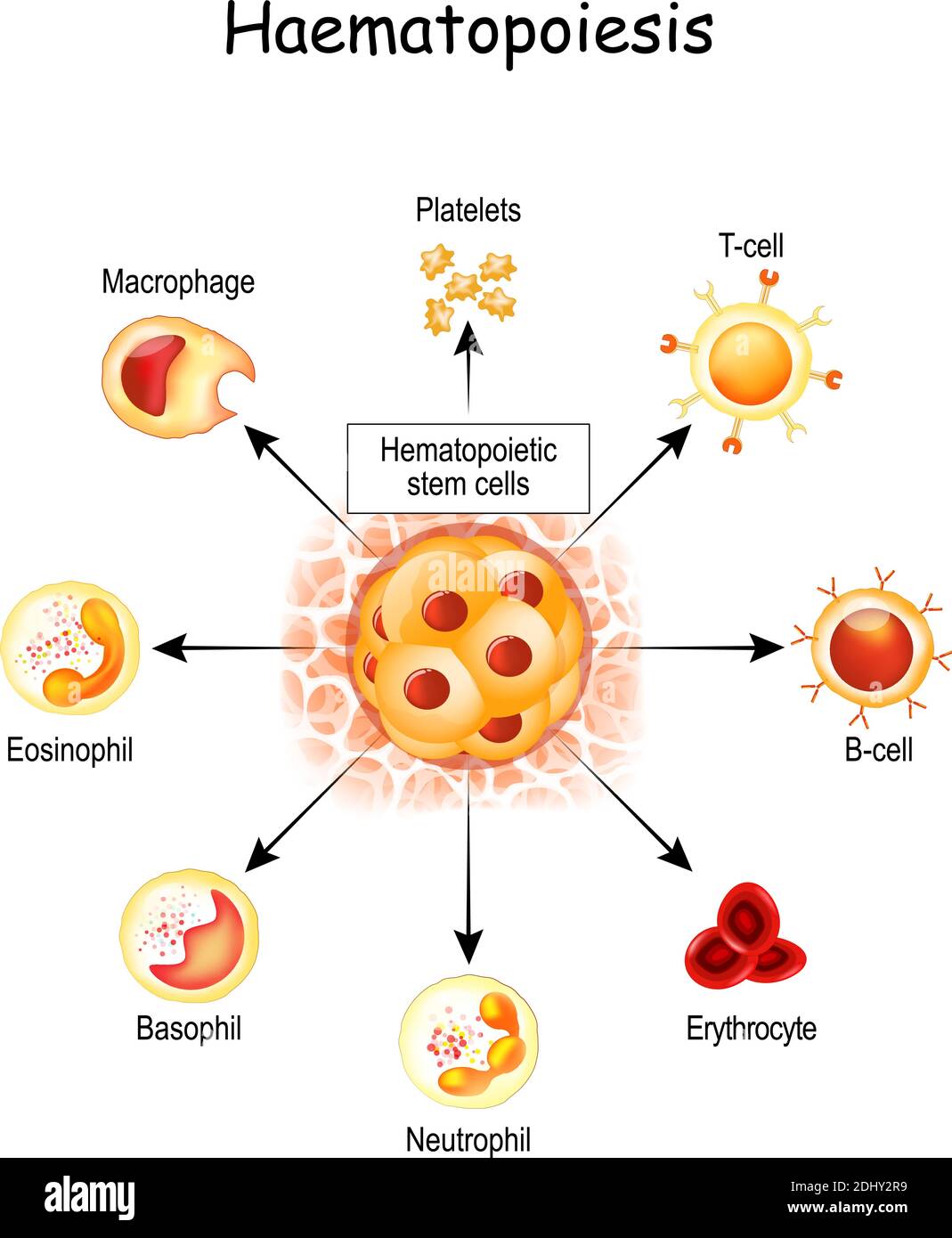
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Hematopoiesis: The Symphony of Blood Cell Production. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!